Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery
Understand the technology of Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery and the process of undergoing Total Knee Replacement (TKR) with LEO-2 the world best Robotic Arm powered by Stryker Mako technology
Play TKR VideoStep 1
Investigation and Segmentation
Before Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery, the X-rays and the CT scan of the patient’s knee is segmented and fed into the robot to obtain a three-dimensional model of the knee joint - the femur, the tibia, and the surfaces that have been damaged by arthritis.
The surgeon with his or her own preferences can then preoperatively plan the best location for the femoral component and tibia component over the model bone, based on factors including patient size, angle of legs, location of articulating surface, and how the femur moves on top of the tibia.
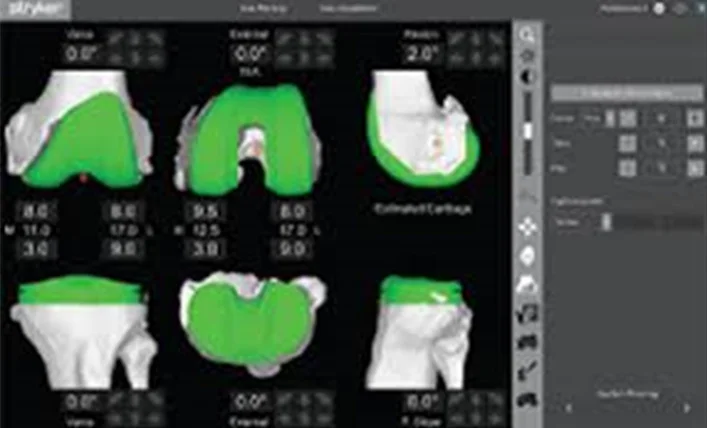
Figure 1 - Pre-Planning and Segmentation of the CT SCAN image
Step 2
Patient specific personalized pre-operative planning
The Robotic Surgeon and his team before the Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery update the robot with the surgery plan, in the operating room the Robotic Surgeon synchronizes & replicates the patient knee movement in the robot screen and makes necessary adjustments before locking in the final plan.
The robot arm will lock the plane of its saw blade into a place relative to the position of the final three-dimensional plan — and assists the surgeon with performing the cuts. The surgeon pushes the saw, but the robot limits where the saw can go in space. It also allows the surgeon to adjust his plan during surgery as needed.
It is important to understand that the surgery is performed by a certified Orthopaedic surgeon like Dr Ashish Singh, who guides the LEO2 robotic arm during the surgery to position the implant in the knee joint.
The robotic arm does not perform surgery or make decisions on its own or move without the surgeon's guidance.
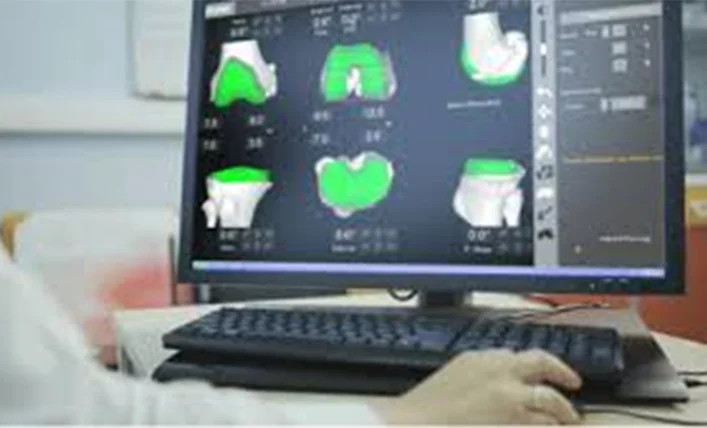
Figure 2 - Pre-Operative Planning stage – virtual bone model
Step 3
Execution of plan during knee surgery within pre-defined limits of haptic boundary
Now the Robotic surgeon can perform the Knee Replacement Surgery using LEO-2 with the accuracy and precision Specific to a Plan & Specific to a Patient, which was not possible before with conventional, manual instruments.
The robot’s haptic boundary prevents soft-tissue trauma. There are several peer-reviewed publications on the benefits, including reduction in post-operative pain, increased patient satisfaction, increased flexion, less opioid drug use; reduction in length of stay, and fewer readmissions due to complications from the procedure has been published.
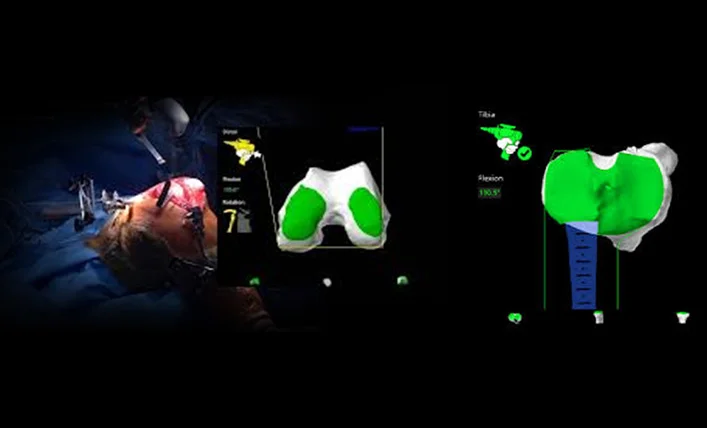
Figure 3 - Accurate position is visualized on a screen whist operating
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery with Leo-2 precision allows for More accurate implant positioning, that may result in a more natural feeling of joint by patient after surgery, Improved safety and reduced risk of injury to adjacent tissues and fast recovery.
Value and Safety Provided by the Pre-Op CT, Small incisions, which can mean a quicker recovery, a shorter hospitalization, and less pain and a potential for better long-term function.
